Environmental groups in Germany are ramping up their opposition to a planned expansion of Tesla’s Gigafactory Berlin-Brandenburg, the U.S. electric vehicle maker’s first manufacturing plant in Europe.
Earlier this week, the factory – which employs around 12,500 people and produces 1,000 EVs per day – was reconnected to the electricity grid after a costly power outage caused by a March 5 arson attack on a nearby pylon, claimed by far-left activists.
Now it faces protests from around 80 climate campaigners belonging to the “Tesla Stoppen” (Stop Tesla) initiative who set up a camp in late February inside 100 hectares of state-owned forest land that Tesla wants to buy and clear for its expansion.
Annika Fuchs, a mobility expert with German climate justice group Robin Wood, told Climate Home she and others occupying the Grünheide forest – who could face eviction from Friday onwards – support local residents’ rejection of the factory expansion in a February referendum.
“We want to make sure that we reduce the amount of cars that we have here in Germany, and really focus on public transport as the solution for the future,” she added.
Both Tesla Stoppen and Grünheide inhabitants issued statements condemning the sabotage of the pylon by the leftist “Volcano Group”, but the incident caught the attention of the German media and has fuelled debate around the potential for EVs to fight climate change.
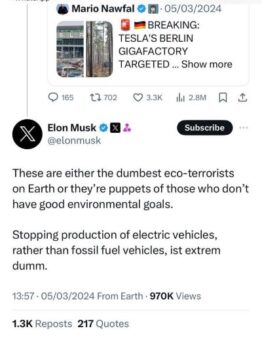
On the day of the pylon attack, Tesla CEO Elon Musk posted on X, the social media platform he owns: “Stopping production of electric vehicles, rather than fossil fuel vehicles, ist extrem dumm” [is extremely stupid].
This week, Musk visited the factory after operations had resumed there, wearing a black T-shirt that read “We are (Giga) the future”, and shouting “Hey, Deutschland rocks! Dig in Berlin for the win!” as he headed back to his car.
Tesla did not respond to a request from Climate Home for comment on opposition to its factory expansion plans.
Water and mineral wars
Tesla’s German gigafactory has been a controversial project even before it began operations in early 2022. Key political figures, eager to bring jobs and tax revenue to the area, have supported the company but local people and climate activists are more sceptical.
Arguments on both sides highlight the contested nature of “green capitalism”. Backers of EVs see them as the best way to cut emissions from fossil fuel-driven transport, while critics decry their energy-intensive production process and the negative environmental and social impacts of battery supply chains for minerals and metals like lithium.
The factory is located five kilometres south of Grünheide, a small town about an hour southeast of Berlin by train. Concerned about its impacts, residents formed a citizen’s initiative that monitors Tesla’s actions in the region.
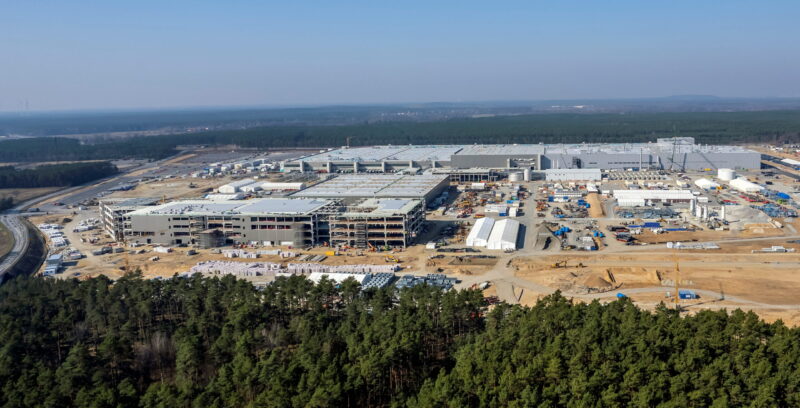

A general view shows the new Tesla Gigafactory for electric cars in Gruenheide, Germany, March 20, 2022. REUTERS/Hannibal Hanschke
German newspaper Stern reported last month that local water authority officials warned Tesla repeatedly that phosphorus and nitrogen levels in the wastewater from its factory released into the nearby River Spree, which flows through Berlin, were found to be six times higher than permitted limits.
Tesla has suggested that concentrations of pollutants in its wastewater are higher because the company reuses water. Tesla’s VP of public policy and business development, Rohan Patel, responded to the claims on X by pointing out that Tesla recycles “up to 100%” of its industrial water, and that the gigafactory uses 33% less water per vehicle than the industry average.
Locals in Grünheide also fear that their drinking water sources may become contaminated if groundwater levels drop too low.
Grünheide is surrounded by lakes and waterways, but as in large swathes of Central Europe, droughts in recent years have left groundwater levels at record lows. Tesla, meanwhile, has become one of the region’s biggest water users. According to German newspaper Tagesspiegel, Tesla used just over 450,000 cubic metres of fresh water last year – although this is less than a third of the amount it was allotted in an agreement with the local water board.
Opponents of the proposed gigafactory expansion note that it would extend the factory into in a water protection area.
At the entrance to the Tesla Stoppen camp, a tall banner hanging from the trees reads “Water is a human right”. Activists at the site told Climate Home that securing the region’s water resources is a key concern – one that also applies further afield.
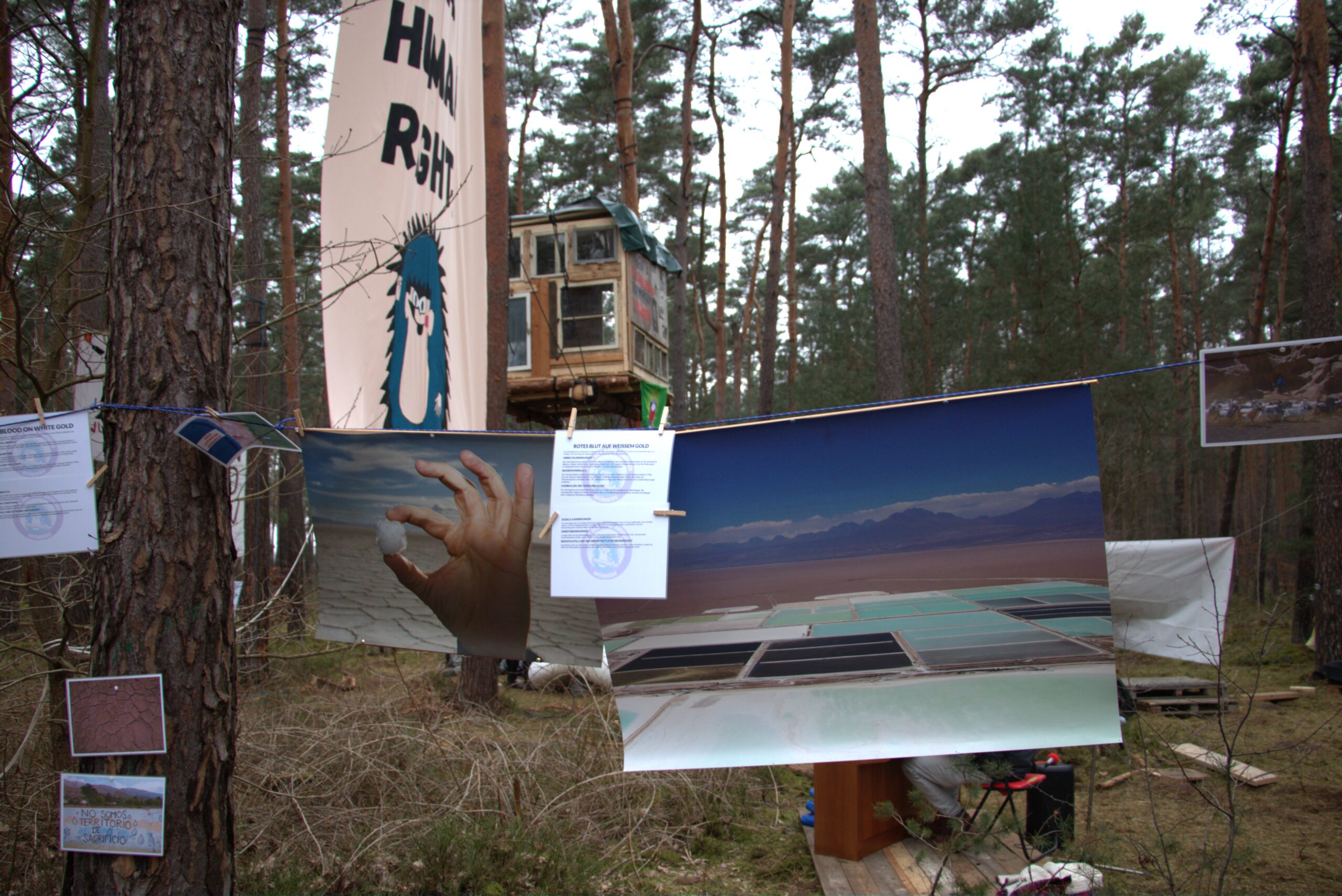

Photos of South American lithium salt flats hang in the Tesla Stoppen protest camp in the Grünheide forest, Germany, March 10, 2024 (Photo: Paul Krantz)
Photographs of South America’s lithium salt flats are hung around the camp, flagging how lithium mining drains water resources from arid regions in Chile, Bolivia and Argentina.
“We see that water injustice and climate injustice are caused by the same reasons. It’s big companies exploiting resources,” said protestor Lamin Chukwugozie.
Stephen Musarurwa, a climate justice advocate from Botswana, said in a speech delivered at a Tesla Stoppen demonstration on Sunday that conflict and environmental damage in the Democratic Republic of Congo is being exacerbated by mining for EV battery components.
“We have communities that don’t own a single electric car, but the amount of destruction is beyond humanity,” he said.

Climate activist Lamin Chukwugozie plays piano at in the Tesla Stoppen protest camp in the Grünheide forest, Germany, March 10, 2024 (Photo: Paul Krantz)
Climate protesters ‘repressed’
The protest camp at Grünheide was initially given permission to remain until March 15, after which local police could move in to evict its occupants.
A police spokesman told the German Press Agency (DPA) it was considering how to deal with the camp but did not say when a decision was expected. Tesla Stoppen is organising workshops to prepare activists on how to respond to an eviction should it happen.
Many of the camp’s members have also been involved in other environmental direct-action movements in Germany, such as the occupation of the site of a lignite coal mine in Lützerath, which attracted Greta Thunberg and other high-profile youth activists in early 2023 and ended in clashes as the site was cleared by riot police and bulldozers.
Here, and before that at the Hambach Forest, campaigners living in tents and treehouses spent years resisting police evictions to stall the expansion of brown coal mines in west Germany – winning a commitment in early 2020 that the Hambach Forest site would not be developed.
In both Lützerath and Hambach, activists reported widespread and brutal police violence used against them. According to a report released this week by global civil society alliance CIVICUS, climate activists face growing restrictions in Germany – as in many other industrialised nations.
“Germany has a reputation of being a country with high protest freedoms, but what we’ve noticed is that not all protests are being treated the same,” Andrew Firmin, who leads climate activism research for CIVICUS, told Climate Home. “Climate protests in particular are being targeted and repressed with excessive force.”
Resistance growing
In Grünheide, as the sun set over the forest after Sunday’s demonstration, Sulti, a Kurdish refugee who did not want to give their full name, admired a wooden platform they and other activists had suspended in a tree about six metres off the ground. Sulti planned to sleep up on the platform, which would be given walls and a roof in the coming days.
Sulti said protestors had come to Grünheide aiming to abolish companies that exploit natural resources and defend shared commons like the forest. “We are trying to build a utopia, and to show people that it’s possible to live in a collective, and to not let the capitalist system push us all into individualism,” the activist said.

Kurdish refugee and protest camp participant Sulti poses in front of a banner at the Tesla Stoppen protest camp in the Grünheide forest, Germany, March 10, 2024 (Photo: Paul Krantz)
Sulti is not afraid of potential confrontation with the authorities, saying: “We are the seed, we are the soil, we are the land, and we will keep growing and growing.”
Chukwugozie pointed to how the climate justice movement has shown it can learn and rebuild after struggles like Lützerath, in which he also participated. “We come back in different places and continue to fight from the ground up,” he said.
Editor’s note: On March 19, an administrative court in Germany rejected a police application to end the camp’s right to legal assembly which had asserted the tree-houses built by protesters were dangerous. After the court decision, the activists said they plan to remain in the forest until at least May 20, DPA reported.
